Gum Recession - Grand Rapids & Wyoming, MI
Comprehensive Gum Recession
Treatment for a Balanced Smile
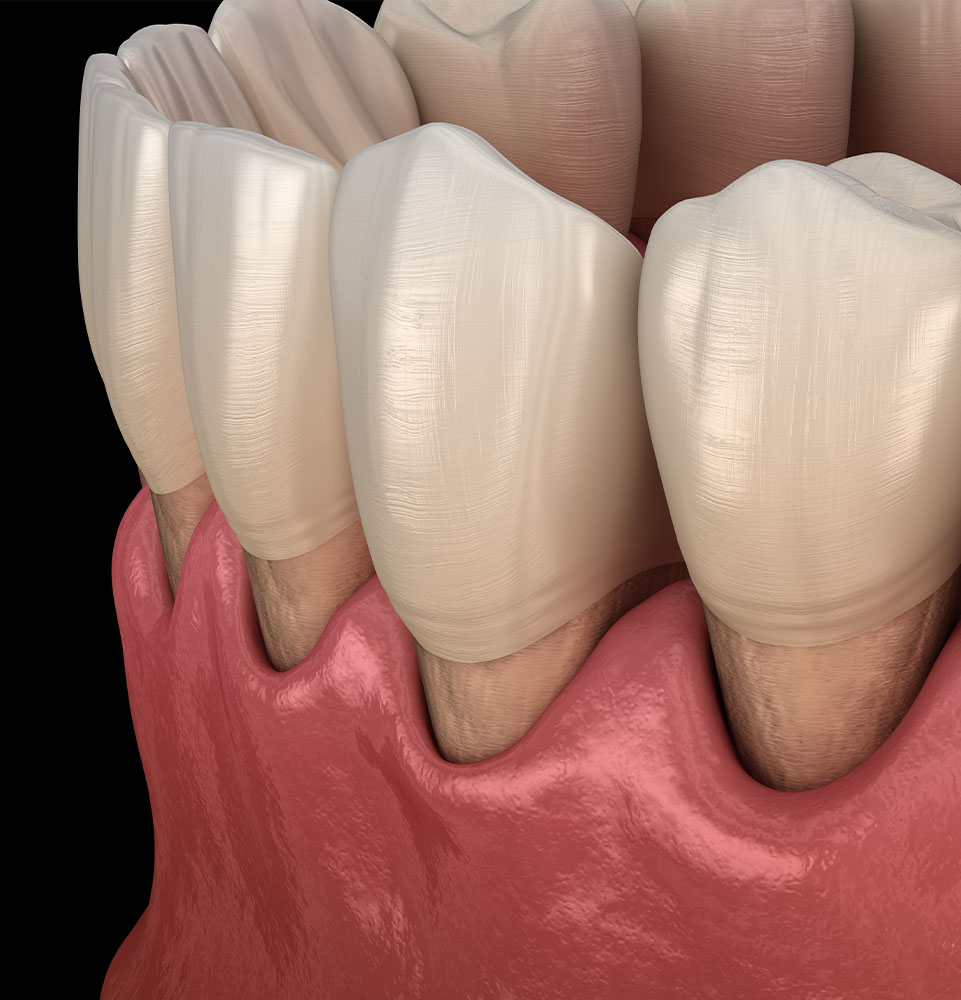
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is when your soft gum tissue retreats toward the tooth roots. This has several negative consequences, both visually and functionally. Receding gums are responsible for about 70% of adult tooth loss. Beyond the emotional visual impact of a receding gum line, your teeth will increase sensitivity towards hot or cold foods/drinks.
If gum recession is making you uncomfortable, don’t ignore the issue. Instead, look to our team at Great Lakes Periodontics for leading solutions to gum loss. As the gum recession advances, conditions can worsen exponentially. Prevent gum disease, tooth loss, loose teeth, unbalanced smile, and jawbone loss with gum recession treatment in Grand Rapids, and Wyoming, MI.

Common Causes of Gum Recession
- Aggressive tooth brushing
- Use of hard-bristled toothbrushes
- Tobacco use
- Periodontal (gum) disease
- Gum tissue trauma
- Thin gum tissue
- Genetic factors
Treating your Receding Gums

Medication
If a gum infection is found, antibiotics may be prescribed. Topical antibiotics can include antibiotic mouth rinses or gels containing medicated relief. Other medications may also treat the underlying problem causing gum recession.
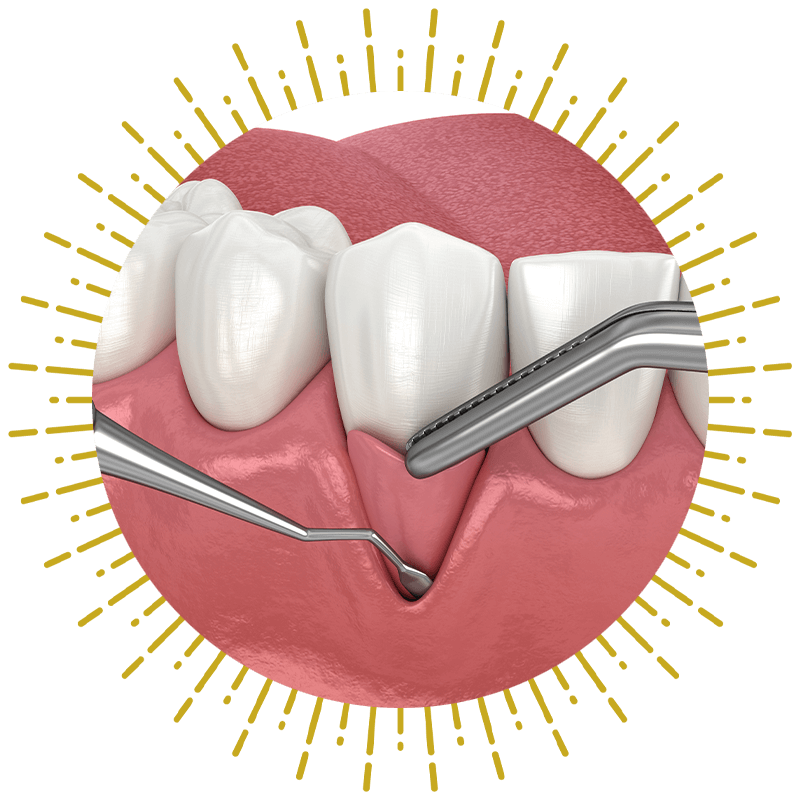
Gum Grafting
Our team can remove a small amount of healthy soft tissue from the roof of your mouth, from in front of any teeth with disproportionate gum coverage, or from another donor source and attach it to the area where your gums have receded. Gum grafting restores your tissue’s protective function, health, and aesthetics.
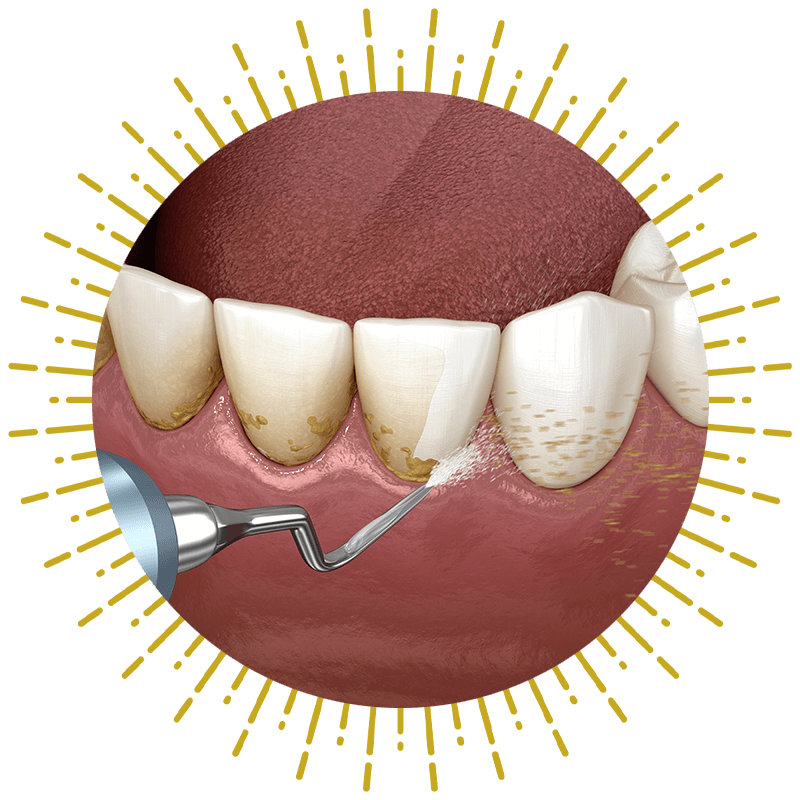
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing are non-surgical treatments often used first in the fight against gum recession caused by gum disease. Scaling removes the bacterial plaque from above and below the gum line, while root planing smooths the tooth surfaces to encourage healthy tissue reattachment and protect against future infection.
